Exploring the Science Behind NiMH Battery Chemistry
Have you ever thought about why your favorite gadgets last longer or charge faster? You use nimh batteries every day in things like cameras, remote controls, and medical devices. These nimh batteries have a special chemistry that makes them different from other rechargeable batteries. The nimh battery uses advanced electrode materials and better sealing. This gives you more energy density and better performance.
You find nimh rechargeable batteries in smart devices and wearables because they charge fast and work well.
Here is how nimh battery technology makes a difference:
Aspect | Statistic / Trend | Significance in Rechargeable Applications |
|---|---|---|
Energy Density | NiMH has better energy density than NiCd, good for medium energy needs | |
Efficiency Rate | 70-80% | Shows these batteries are reliable and last in many uses |
Market Share (Electrode Segment) | 48% in 2023 | Shows electrodes are very important for battery performance |
Small-sized NiMH Batteries Revenue Share | ~59% in 2023 | Shows nimh batteries are common in electronics, medical tools, and small devices |
Regional Revenue Share (North America) | ~41% in 2023 | Shows high demand in electronics, cars, and renewable energy in this area |
Fastest Growing Market Region | Asia-Pacific (2024-2032) | Growth comes from more factories, electric cars, and electronics |
Application Trends | More use in electronics, power tools, hybrid cars, wearables, IoT | Shows nimh batteries are used in more things and are getting better |
Technological Advancements | Better energy density, longer life, safer for the environment | Helps nimh batteries stay popular and grow in the market |
Nimh batteries help meet the need for green, rechargeable, and strong power sources. You can find nimh technology in many places, from home gadgets to hybrid cars. This NiMH (Nickel-Metal-Hydride) Battery: A Complete Guide will help you learn about the science behind the batteries you use every day.
Key Takeaways
NiMH batteries use nickel and metal hydride materials. These materials help them store and give out energy safely. They do this in an efficient way.
NiMH batteries give more energy than old NiCd batteries. They are safer and better for the earth.
NiMH batteries charge quickly. They can last for hundreds or even thousands of cycles. They work well in things like cameras, toys, and hybrid cars.
Taking care of NiMH batteries is important. Use the right charger. Store them in cool and dry places. This helps them last longer and stay healthy.
NiMH batteries have safety features built in. They have vents and strong cases. These stop them from getting too hot or breaking.
NiMH batteries cost less than lithium-ion batteries. They are safer but hold less energy. They also charge slower.
New materials and smart charging are making NiMH batteries better. They are becoming stronger and last longer.
Recycling NiMH batteries gets back useful metals. It helps keep the earth clean. This supports a greener future.
NiMH (Nickel-Metal-Hydride) Battery: A Complete Guide
What Is NiMH?
You may ask what makes a nimh battery special. This battery has a unique chemistry. It uses a nickel oxyhydroxide cathode. It also uses a hydrogen-absorbing metal alloy anode. The electrolyte is a strong alkaline solution. Most of the time, it is potassium hydroxide. When you charge or use the battery, a chemical reaction happens. This reaction can go forward and backward. It happens between the nickel and the hydrogen-storing alloy. Because of this, the battery can store and give out energy many times.
The main reaction inside a nimh battery is:
H₂O + M + Ni(OH)₂ ⇌ OH⁻ + MH + NiOOH
Nimh batteries come in many shapes and sizes. Each cell usually gives 1.2 volts. Their capacity can be from 1000mAh to over 3000mAh. You can recharge them hundreds of times. This makes them a good choice for things you use every day.
Here are some important features of nimh batteries:
High energy density for portable devices
No memory effect, so you do not lose capacity if you recharge before empty
Safe and stable, with less risk of overheating
More eco-friendly than batteries with toxic metals
Why NiMH Matters
You use nimh batteries in many things at home and work. They power cameras, toys, remote controls, and hybrid cars. The nimh (nickel-metal-hydride) battery: a complete guide explains why these batteries are important today.
Nimh batteries have about 40% more energy density than nickel-cadmium batteries. They do not have toxic cadmium, so they are safer for the environment. Nimh batteries cost less than lithium-ion batteries. They are also less likely to overheat. They work well in high-drain devices like power tools and some medical equipment.
Parameter | Consumer Grade | Industrial Grade |
|---|---|---|
Energy Density | 60-120 Wh/kg | 80-140 Wh/kg |
Cycle Life | 500-800 cycles | 1,200-2,000 cycles |
Self-Discharge | 20%/month | 10%/month |
Operating Temp | -20°C to 45°C | -40°C to 60°C |
Nimh batteries can last a long time if you take care of them. They can work for 10 to 15 years with good use. You should use the right charger. Do not overcharge them. Store them in a cool, dry place. Always choose the right size and capacity for your device.
Nimh (nickel-metal-hydride) battery: a complete guide helps you see why nimh batteries are everywhere. They give you reliable, rechargeable power for daily use. They also help cut down on waste and protect the environment. When you pick nimh rechargeable batteries, you make a smart and responsible choice.
Battery Chemistry
To know how a nimh battery works, you need to look at its chemistry. You see this every time you use a nimh battery in a camera or remote. The science inside each cell makes nimh batteries strong and dependable. Let’s look at the materials and reactions that make this happen.
Electrode Materials
A nimh battery has two main electrodes. Each one helps store and give out energy.
Nickel Oxyhydroxide Cathode
The cathode is made from nickel oxyhydroxide (NiOOH). This material changes during charging and using the battery. When you charge it, the nickel oxyhydroxide takes in electrons and stores energy. When you use the battery, it gives up electrons and releases energy. Scientists add things like cobalt or rare earth metals to the cathode. These help the battery last longer and work better. The additives help the cathode change in each cycle. They also help the battery keep its power after many uses.
Tip: The nickel oxyhydroxide cathode helps the nimh battery have high energy and last a long time.
Metal Hydride Anode
The anode uses a metal hydride alloy. This alloy can take in and let go of hydrogen. When you charge the battery, the alloy soaks up hydrogen atoms. When you use the battery, it lets the hydrogen out. The kind of alloy in the anode changes how much energy the battery can hold. It also changes how many times you can recharge it. Scientists have tried many alloys, like LaNi5 and other rare earth mixes, to find the best one. Some alloys do not rust as fast, so the battery lasts longer. Others help hydrogen move in and out more easily, which makes the battery work better.
You get safer and stronger nimh batteries because of these new materials. They also give steady power.
Electrolyte Role
The electrolyte in a nimh battery is usually potassium hydroxide (KOH). This liquid lets ions move between the electrodes. The electrolyte does not join in the main reaction, but it is still very important. The right kind and amount of electrolyte help the battery charge fast and last longer. If the electrolyte is too weak or too strong, the battery may lose power or wear out faster.
Studies show that KOH works best for nimh batteries, especially with AB5-type metal hydride alloys. Other electrolytes, like CsOH or NaOH, do not work as well. The table below shows how different electrolytes change hydrogen movement and battery power:
Electrolyte Type | Hydrogen Diffusion Coefficient (cm²/s) | Electrode Capacity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
KOH | 4.65 × 10⁻¹⁰ | Highest | Best for AB5-type alloys |
CsOH | Lower than KOH | Lowest | Least effective |
LiOH, NaOH, RbOH | Intermediate values | Intermediate | Not as good as KOH |
You can see that the right electrolyte helps nimh batteries give more power and last longer. Things like temperature, how much electrolyte there is, and how you charge the battery also matter.
Chemical Reactions
The most important part of nimh battery chemistry is its reactions. When you use the battery, the metal hydride anode gives up hydrogen. The nickel oxyhydroxide cathode takes in electrons. The main reactions are:
At the cathode:
NiOOH + H₂O + e⁻ → Ni(OH)₂ + OH⁻At the anode:
MH + OH⁻ → M + H₂O + e⁻
(M stands for the metal alloy)Overall reaction:
MH + NiOOH → M + Ni(OH)₂
These reactions can go both ways. That means you can recharge the nimh battery many times. The materials inside switch back and forth, so they can store and give out energy when you need it.
Scientists use special tools to watch these reactions. For example, they use mass spectrometry and Raman spectroscopy to see gases like hydrogen and oxygen inside the battery. If you overcharge a nimh battery, hydrogen and oxygen gases build up. The battery can turn these gases back into water. This keeps the battery safe and helps it last longer.
Tests with nimh batteries show that the way the electrodes and electrolyte work together changes how much energy you get and how long the battery lasts. Tests on AA-size nimh cells show that the right alloy and electrode design can stop rust and keep the battery working for hundreds or thousands of cycles. These results show that nimh battery chemistry is strong and dependable.
Note: The special battery chemistry in nimh batteries makes them great for things like hybrid cars and power tools.
Structure

Cell Design
If you open a NiMH battery, you see a clever setup. The metal case holds all the main parts inside. The positive electrode is made of nickel hydroxide. The negative electrode is a metal alloy that stores hydrogen. These two electrodes are very close together. A separator sits between them. The separator stops the electrodes from touching. It lets ions move when charging or using the battery.
The electrolyte is usually 30% potassium hydroxide. It fills the space and helps ions move around. This design gives each cell a voltage of 1.2 volts. When the battery is fully charged, the voltage can go up to about 1.55 or 1.6 volts. The battery can be used until it drops to 1.0 volt. Then it needs to be charged again.
There are two main types of metal alloys in the negative electrode. AB5 alloys use rare earth elements and nickel. These help lower self-discharge and cost. AB2 alloys use titanium, vanadium, or zirconium. These give the battery more energy density. Some batteries add lithium hydroxide to the electrolyte. This helps the positive electrode work better.
Here is a table with important design facts for a NiMH battery cell:
Component/Metric | Description/Value |
|---|---|
Battery Type | 3.6 V, 700 mAh NiCd/NiMH cell |
Charging Circuit | Uses LM317 adjustable regulator; charging current ≈ 700mA (switch open), ≈ 1A (switch closed) |
Discharging Circuit | Discharge current ≈ 320 mA with 11 Ω resistor and 3.6 V battery voltage |
Internal Resistance Measurement | Two-pulse method based on direct current discharge |
Key Parameters Measured | Internal resistance, charging current, discharging current, voltage |
Control System | Microprocessor-based controller for charging/discharging and measurement |
Data Acquisition & Server | Data sent via USB/TCP-IP to MySQL database; online monitoring with PHP-based website |
You see this kind of battery in many places. For example, the Toyota Prius uses a 1.3 kWh NiMH battery pack. This shows the design works well in big, real-life uses.
NASA found that storing batteries for a long time can make them lose some power. The battery might show higher but steady voltages and pressures. Charging slowly, like trickle charging, helps stop permanent damage. Testing how many times you can use the battery helps engineers make better designs.
Internal Resistance
Internal resistance is very important for how your battery works. It shows how much energy turns into heat inside the battery. If the resistance is low, the battery gives more power and stays cooler.
Small NiMH batteries have about 20 milliohms of internal resistance. Bigger batteries can have more resistance. The table below shows the resistance for different battery types:
Battery Type | Internal Resistance (mOhm) |
|---|---|
NiMH | |
NiCd | 155 |
Lithium-ion | 320 |
NiMH batteries have higher resistance than NiCd and lithium-ion batteries. This means they cannot charge or discharge as fast. They also make more heat.
Internal resistance changes depending on how full the battery is. When the battery is almost empty or just charged, resistance is highest. At half charge, resistance is lowest. If you let the battery rest after charging, resistance gets better.
State-of-Charge Condition | Internal Resistance Behavior in NiMH Batteries |
|---|---|
Low state-of-charge | Highest internal resistance |
Immediately after charge | High internal resistance |
Half charge | Lowest internal resistance |
After resting post-charge | Improved (lower) internal resistance |
You can check internal resistance with a two-pulse test while the battery is working. This helps you know if the battery is healthy. If resistance is high, the battery may be old or damaged. High resistance also means more heat and less power for your device.
Tip: Keep your battery cool and do not let it run out all the way. This helps lower resistance and makes your battery last longer.
Battery Performance
Capacity
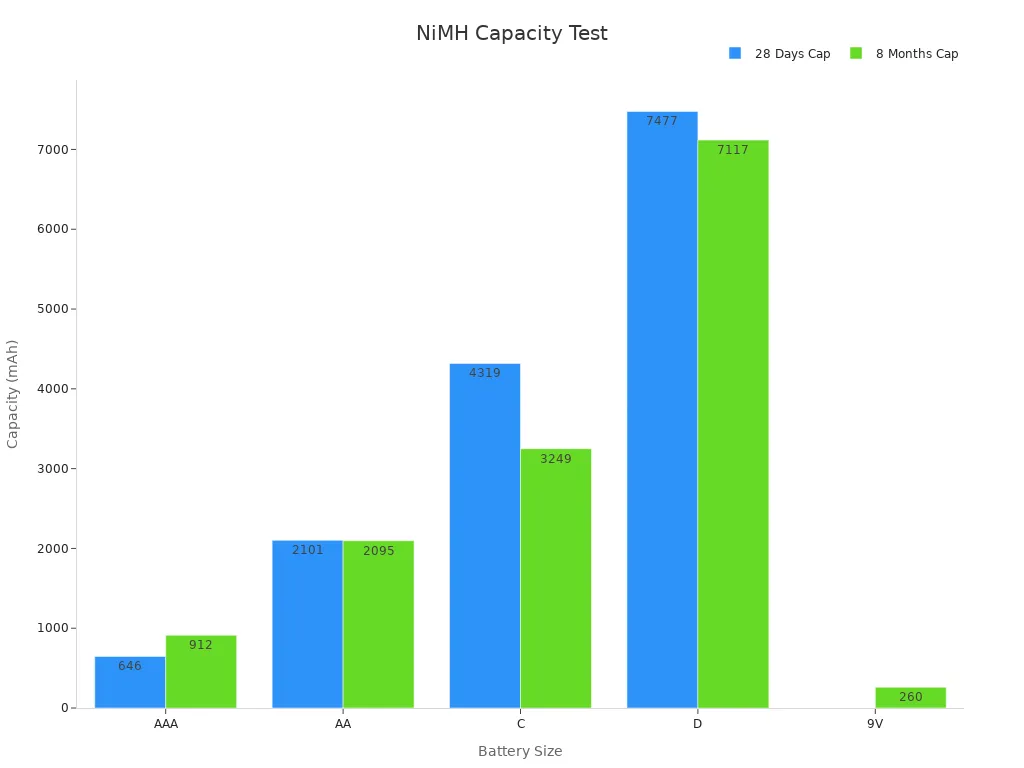
When you pick a nimh battery, you want to know how much energy it holds. This is called capacity. Capacity is measured in milliampere-hours (mAh) or ampere-hours (Ah). A bigger number means your device works longer. Nimh batteries are a good mix of size and energy. You see nimh batteries in AA, AAA, C, D, and 9V sizes. Each size has its own capacity.
Companies test nimh batteries to check if they meet their listed capacity. For example, a AAA nimh battery usually has 650 mAh. After 28 days, it still has about 646 mAh. Even after 8 months, it can reach up to 912 mAh. This shows the battery stays healthy and does not lose much power. AA nimh batteries start at 2500 mAh and keep over 2100 mAh after months. Nimh batteries keep most of their energy even after a long time.
Battery Size | Rated Capacity (mAh) | Capacity After 28 Days Storage (mAh) | Capacity After 8 Months Storage (mAh) | Discharge Duration (h) | Columbic Efficiency (%) | Endurance Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
AAA | 650 | 646 | 912 | >3 (28 days), >4 (8 months) | N/A | 300 |
AA | 2500 | 2101 | 2095 | >3 (28 days), >4 (8 months) | N/A | N/A |
C | N/A | 4319 | 3249 | >3 (28 days), >4 (8 months) | N/A | N/A |
D | N/A | 7477 | 7117 | >3 (28 days), >4 (8 months) | 70-78 | N/A |
9V | N/A | N/A | 260 | >3 (28 days), >4 (8 months) | 58-62 | N/A |
Nimh batteries meet or beat the IEC 61951-2 rules for capacity and use. High energy density means you get more power in a small battery. This makes nimh batteries great for cameras, toys, and other small things. They also last a long time and do not lose much power.
Cycle Life
You want your nimh battery to work for many uses. Cycle life tells you how many times you can charge and use a battery before it gets weak. Nimh batteries can last for hundreds or even thousands of cycles. This is because of their strong chemistry and design.
Tests show AAA nimh batteries can handle at least 300 cycles. This is more than the IEC minimum of 200 cycles. Some nimh batteries for industry can go up to 2,000 cycles. This means you can use your battery for years. You get steady power for your devices, even if you use them a lot or just sometimes.
Nimh batteries work well in many situations. Studies using EIS show nimh batteries act as high pass filters. High-frequency AC signals do not make them age faster. This means nimh batteries stay healthy and last long, even in tough jobs like hybrid cars or grid storage.
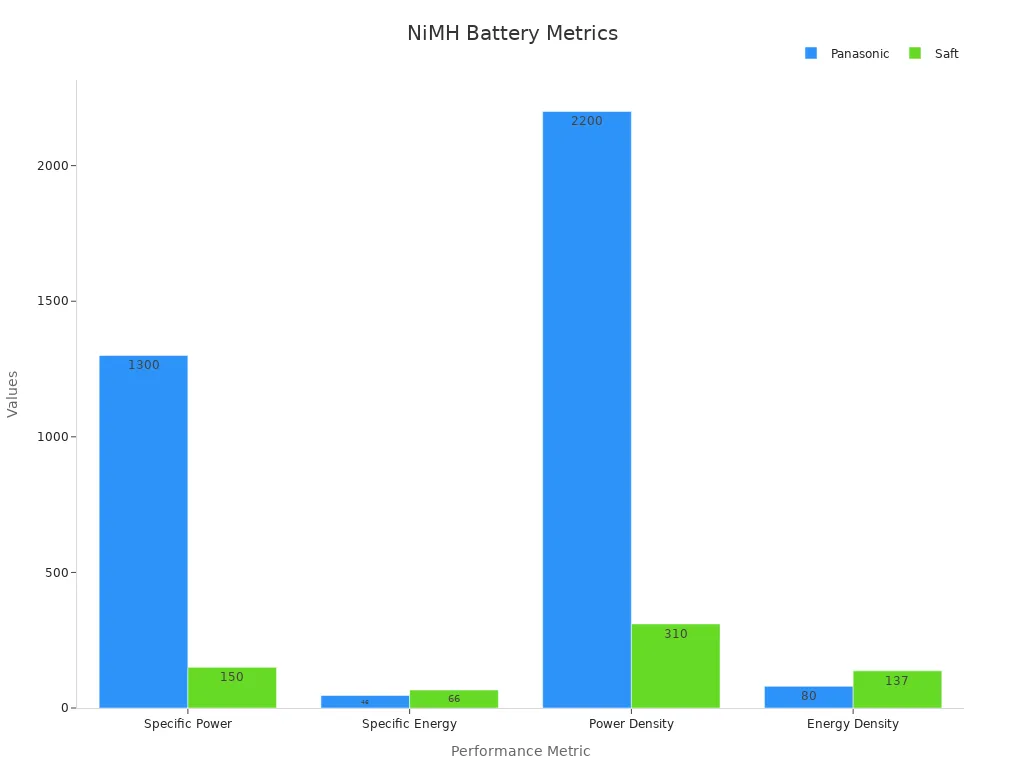
Panasonic Module (Toyota Prius) | Saft NHE 10-100 Module | Theoretical Max (Linden) | |
|---|---|---|---|
Specific Power (W/kg) | 1300 | 150 | N/A |
Specific Energy (Wh/kg) | 46 | 66 | 240 |
Power Density (W/L) | 2200 | 310 | N/A |
Energy Density (Wh/L) | 80 | 137 | N/A |
You see nimh batteries in hybrid cars because they give high power and energy. They also last a long time and are safe. The main problems are weight and lower voltage, but the long life and low loss make nimh batteries a smart pick for many things.
Self-Discharge
Self-discharge means how much energy a battery loses when not used. Nimh batteries lose charge faster than lithium-ion, but new designs are better. Now, nimh batteries can keep most of their charge for weeks or months.
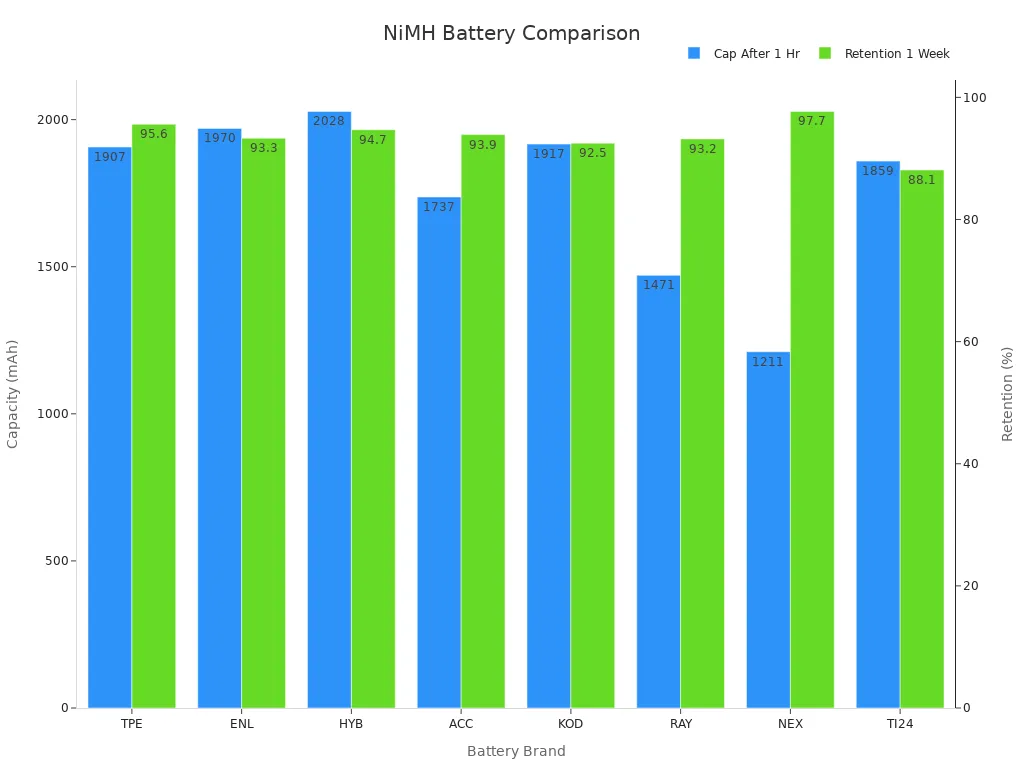
You check self-discharge by seeing how much power is left after storage. After one week, many nimh brands keep over 90% of their power. The table below shows how different brands do:
Battery Brand | Capacity After 1 Hour (mAh) | Capacity Retention After 1 Week (%) |
|---|---|---|
TPE | ~1907 | 95.6% |
ENL | ~1970 | 93.3% |
HYB | ~2028 | 94.7% |
ACC | ~1737 | 93.9% |
KOD | 1917 | 92.5% |
RAY | 1471 | 93.2% |
NEX | 1211 | 97.7% |
TI24 | 1859 | 88.1% |
Nimh batteries from different brands show good health and low self-discharge. The self-discharge rate depends on temperature and how long you store them. Cooler places and shorter storage help slow battery loss. The main reason for self-discharge is hydrogen leaving the metal hydride anode. New microencapsulation methods help slow this and make batteries last longer.
You can use nimh batteries in many things and trust they will keep their charge. This makes them good for remotes, flashlights, and emergency kits. You get steady power and do not have to worry about losing charge quickly.
Safety
You want your batteries to be safe in every device you use. NiMH batteries give you strong safety features. You do not have to worry about fires or explosions like with some other battery types. The chemistry inside NiMH batteries helps prevent dangerous reactions. You get peace of mind when you use them in toys, cameras, or even hybrid cars.
NiMH batteries use a water-based electrolyte. This makes them less likely to catch fire. If you overcharge a NiMH battery, it can release gas. The battery has a special vent to let this gas out safely. You should always use the right charger. This helps keep battery health at its best. If you use a charger made for NiMH batteries, you lower the risk of overheating.
Tip: Always check your charger and battery for damage before use. This simple step protects battery health and keeps you safe.
Here are some key safety features you find in NiMH batteries:
Pressure relief vents: These let out gas if pressure gets too high.
Strong metal casing: This protects the battery from bumps and drops.
Separator material: This keeps the positive and negative parts apart, stopping short circuits.
Built-in temperature sensors: Some batteries have these to stop charging if they get too hot.
You can help battery health by storing your batteries in a cool, dry place. Heat can damage the inside parts. If you see a battery that looks swollen or leaks, you should stop using it. Recycle old or damaged batteries at a proper center. This keeps you and the environment safe.
A table below shows how NiMH batteries compare to other types for safety:
Battery Type | Fire Risk | Gas Release | Overcharge Protection | Battery Health Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
NiMH | Low | Yes (vented) | Good | High |
NiCd | Low | Yes (vented) | Good | Medium |
Li-ion | Medium | No | Needs electronics | Medium |
Alkaline | Very Low | No | Not rechargeable | Low |
You can see that NiMH batteries offer a good balance of safety and battery health. You do not need complex electronics to keep them safe. You just need to follow simple rules. Do not mix old and new batteries. Do not try to open or fix a battery yourself. Always use the right charger.
If you want to keep battery health strong, you should avoid deep discharges. Try not to let your battery run out all the way. Charge it before it gets too low. This helps battery health and makes your battery last longer.
Note: Good battery health means better battery performance and safer use every day.
Comparison with Other Batteries

NiMH vs. NiCd
When you look at nimh and nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries, you notice some big differences. Nimh batteries can hold about 30-40% more energy than NiCd. This means your devices can work longer before you need to charge them again. Nimh batteries do not have much memory effect. You do not have to drain them all the way before charging. They are also better for the environment because they do not have toxic cadmium.
Nimh batteries lose charge faster. You might lose 20% of power on the first day and about 10% each month after.
Some new nimh batteries, like Eneloop, keep their charge much longer.
You must be careful when charging nimh batteries. They can get hot if you overcharge them.
NiCd batteries work better in very cold places and are tougher.
If you take care of NiCd batteries, they can last longer, but they do not hold as much energy and are worse for the environment.
Tip: If you want more power and want to help the planet, nimh batteries are a better pick than NiCd.
NiMH vs. Li-ion
You see nimh and lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries in many things. Both types have good and bad points. Nimh batteries cost less at first and are easier to recycle. They are also safer and do not catch fire easily. Li-ion batteries can hold more energy and give more power. Phones and laptops use Li-ion because they need lots of energy in a small battery.
Here is a table to help you see the differences between nimh and Li-ion batteries:
Performance Metric | NiMH Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
Energy Density | Lower energy density | Higher energy density |
Power Density | Lower power density | Higher power density |
Cycle Life | 2-5 years | 5 years or more (2-5 times longer lifespan) |
Charging Speed | Slower, sensitive to overcharging | Faster, supports quick-charge |
Self-Discharge Rate | Higher, faster loss in heat | Lower self-discharge |
Memory Effect | Present, reduces capacity | Minimal or none |
Cost | Lower upfront | Higher, but lasts longer |
Safety | More stable, less sensitive to heat | Sensitive to heat, risk of thermal runaway |
Recycling | Easier, less hazardous materials | Harder, more toxic materials |
Applications | Hybrid cars, electronics, medical devices | Electric vehicles, phones, grid storage |
Nimh batteries are good for hybrid cars and medical tools. Li-ion batteries are best for phones and electric cars because they hold more energy and charge quickly.
Pros and Cons
It is important to know the good and bad sides of nimh battery before you buy one. Nimh batteries give you good energy, are safe to use, and are easy to recycle. They cost less than Li-ion and are not as harmful as NiCd. You can use them in many things, like cameras and hybrid cars.
Pros:
More energy than NiCd
Better for the environment
Lower cost at first
Safe and steady performance
Cons:
Lose charge faster than Li-ion and NiCd
Charge slower and can get hot if overcharged
Do not hold as much energy as Li-ion
Do not last as long if used a lot
Note: Nimh batteries give you safe, low-cost, and steady power. They work well for daily use, but you will need to charge them more often than Li-ion.
Challenges and Improvements
Heat and Gas Generation
When you use or charge a NiMH battery, it can get hot. Gas can also build up inside the battery. This happens because the reactions inside are not perfect. Charging too fast or too long makes the battery hotter. The battery can let out hydrogen and oxygen gases. If these gases build up, pressure goes up. Most NiMH batteries have vents to let out extra gas and keep you safe.
You can help by charging the battery the right way. Charging slowly keeps the battery cool. Fast charging makes more heat and gas. Too much heat or gas can damage the battery over time. The battery will not last as long or hold as much energy. Always check your charger and battery for damage before charging. If you see swelling or leaks, stop using the battery.
Tip: Keep your batteries in a cool, dry place. Do not charge them in hot spots to avoid heat and gas problems.
Charge Algorithms
Charging a NiMH battery is harder than charging other types. You need smart charging methods to get the best results. These methods watch for signs that the battery is full. They look at voltage drops, temperature changes, and charging time. Some chargers use negative delta voltage detection. Others use temperature limits or timers.
Step-differential charging can make your battery hold about 6% more energy. But charging too hard can damage the battery faster. You want to balance fast charging with battery life. Some studies show constant power charging (CPCV) works better than constant current charging (CCCV). CPCV saves energy and keeps the battery healthier. It also helps the power grid when many batteries charge at once.
Smart charging can change the charging speed based on how well it works. This helps your battery last longer and stay cool. Special sensors, like hydrogen sensors, tell the charger when to stop. This keeps the battery from overcharging and slows damage. You get a longer-lasting battery and better performance.
Note: The right charging method helps you avoid overcharging, overheating, and early battery damage.
Material Advances
You get better NiMH batteries because of new materials. Scientists have made big improvements in energy and power. In 1991, small NiMH cells had about 54 Wh/kg of energy. Now, they can go over 100 Wh/kg. Power has also gone up from under 200 W/kg to 1200 W/kg. Some new batteries can even reach 2000 W/kg.
Metric / Innovation | Description / Improvement |
|---|---|
Specific Energy | Went from 54 Wh/kg (1991) to over 100 Wh/kg (now) |
Specific Power | Grew from under 200 W/kg to 1200 W/kg; up to 2000 W/kg in new designs |
Operating Temperature Range | Works well even at -30 °C |
Nickel Hydroxide Composition | Mixes gamma and beta phase nickel hydroxide for more capacity |
Modifier Elements | Added to help charging, especially when it is hot |
Conductive Additives | Filamentary nickel helps electricity move inside the battery |
Cobalt Encapsulation | Keeps voltage steady and lowers cost |
Surface Engineering of Metal Hydride Alloys | Tiny nickel alloy bits help reactions and lower resistance |
You see better battery performance because of these new materials. New materials help the battery charge faster and last longer. They also help the battery work in cold weather. Special coatings and additives protect the battery from damage. This means you get more cycles and safer use. Engineers keep finding ways to make NiMH batteries stronger and more reliable for you.
Future Outlook
Applications
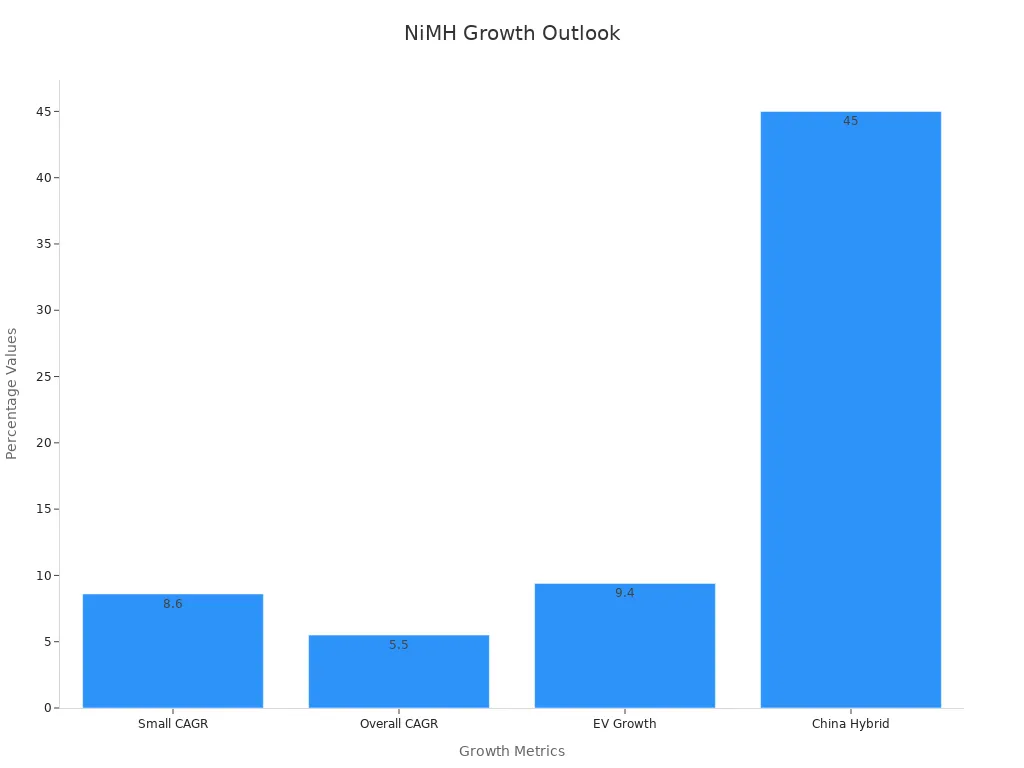
Nimh batteries will show up in more places as tech grows. The market for small nimh batteries will double from $1.23 billion in 2024 to $2.45 billion by 2033. The whole nimh market will reach about $3.5 billion by 2033. This growth happens because of new uses in electric cars, green energy storage, and smart gadgets. You can find nimh batteries in hybrid cars, power tools, and medical gear. These batteries give steady power and last a long time.
Usage and Market Drivers | |
|---|---|
Automotive | Hybrid electric vehicles need nimh batteries for safety and energy density |
Emergency Power Backup | Used in homes, factories, and offices for long-lasting rechargeable energy |
Consumer Electronics | Digital cameras, cordless phones, and medical devices use nimh for steady performance |
Industrial | Tools, robotics, and smart meters rely on nimh for longevity and fast charging |
Renewable Energy Storage | Solar and wind systems use nimh batteries for backup and grid support |
You will see nimh batteries in Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe. China makes the most, with 34% of all nimh batteries. Hybrid car sales in China went up by 45% in 2024. The need for nimh batteries in electric cars is growing by 9.4% each year. You will also find nimh batteries in smart grids and backup power for green energy.
Nimh batteries give a good mix of energy, safety, and long life. You can recharge them many times, and they work in hot or cold places. These things make nimh batteries a great pick for new uses.
Research Trends
Nimh battery research will focus on better materials and smarter designs. Experts want to make energy density 10-15% higher in five years. They also hope to make batteries last 20% longer with new electrode materials and better ways to build them. You will get safer batteries with better heat control and pressure relief.
Note: New rules for the environment make companies use recycled metals and safer parts in nimh batteries.
Scientists are working to help nimh batteries compete with lithium-ion. Nimh batteries still cost less, are safer, and work better in the cold. You will see more nimh batteries in hybrid cars and portable gadgets. Companies like Panasonic and FDK are leading in new ideas and making nimh batteries.
Here are some big research trends you should know:
New electrode materials for more energy and longer life
Better electrolyte mixes for faster charging and better use
Smarter charging systems to keep batteries healthy
More recycling and use of earth-friendly parts for the planet
Improved safety to stop overheating and leaks
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Market Growth Forecast | 5-7% CAGR from 2025 to 2033, led by electronics, renewable energy, and HEVs |
Energy Density Improvement | 10-15% increase targeted in five years |
Cycle Life Enhancement | 20% longer longevity expected with new materials |
Safety Features | Better thermal management and pressure relief |
Environmental Regulations | More recycled metals and fewer hazardous substances |
Key Market Players | FDK, Panasonic, YUASA leading innovation |
Nimh batteries will become even more important as the world uses more clean energy and smart devices. The focus on rechargeable power, energy, and long life will keep nimh batteries at the heart of new technology.
You have learned that nimh batteries use special chemistry for safe power. These batteries are good for everyday things and green energy. When you know about nimh battery chemistry, you see why they last long and stay safe. Nimh batteries help you recycle and save metals that matter.
Nimh batteries have been recycled for a long time, which helps reuse materials.
More nickel and cobalt are needed for nimh batteries, so recycling is even more important.
Recycling nimh batteries can get back over 85% of the nickel and cobalt.
Nimh battery recycling helps keep the planet clean and gives a steady supply of metals.
Nimh batteries will become more popular as technology and recycling get better. You can help by picking nimh batteries and recycling them. What you do helps make the future greener with nimh power.
FAQ
What devices use NiMH batteries?
You find NiMH batteries in cameras, remote controls, toys, cordless phones, and hybrid cars. Many medical devices and power tools also use them. You can use NiMH batteries in most gadgets that need AA, AAA, C, D, or 9V batteries.
How do you store NiMH batteries for best results?
You should store NiMH batteries in a cool, dry place. Charge them to about 40-60% before storing. Avoid extreme heat or cold. If you store them for a long time, recharge them every few months to keep them healthy.
Can you mix NiMH batteries with other types?
Never mix NiMH batteries with other battery types in the same device.
You risk leaks, poor performance, or damage. Always use the same type, brand, and charge level for best results.
How long does it take to charge a NiMH battery?
Charging time depends on the battery size and charger. Most AA or AAA NiMH batteries take 2 to 6 hours with a standard charger. Fast chargers can finish in 1 to 2 hours. Always follow your charger’s instructions.
Do NiMH batteries have a memory effect?
You do not need to worry about memory effect with NiMH batteries. You can recharge them at any time. They do not lose capacity if you charge them before they are empty.
Are NiMH batteries safe to use?
NiMH batteries are safe for daily use. They have vents to release gas if pressure builds up. You should use the correct charger and avoid overheating. If a battery leaks or swells, stop using it and recycle it properly.
How can you recycle NiMH batteries?
You can recycle NiMH batteries at many electronics stores or recycling centers. Look for battery recycling bins in your area. Recycling helps recover metals and protects the environment.
See Also
A Guide To Identifying And Selecting L1154 Battery Alternatives
Top Tips For Choosing The Right LR41 Battery Replacements
Comparing 21700 And 18650 Batteries For Flashlight Performance
