Expert Advice on Selecting the Right Fiber Optic Connector
Picking the right fiber optic connector is very important. A bad choice can cause problems like signal loss or system failure. You must choose connectors that fit your needs for smooth connections. The right connector also saves money by avoiding extra fixes or upgrades. Think about things like how well it fits, how strong it is, and how it works. By focusing on these, you can get good quality without spending too much.
Key Takeaways
Picking the right fiber optic connector stops signal problems.
Match the connector to your fiber type. Single-mode works for long distances, and multi-mode is good for short ones.
SC connectors are strong and useful, great for telecom and data centers.
LC connectors are small and fast, perfect for setups needing high speeds.
Clean and check connectors often to keep them working well.
Think about where connectors will be used. Outdoor ones must handle bad weather.
Spending more on good connectors now saves money later by lasting longer.
Ask experts if you're unsure. The right choice makes your system work better.
Understanding Fiber Optic Connectors
What Are Fiber Optic Connectors?
Fiber optic connectors are tiny tools that link two fiber cables. They let light signals pass through smoothly for data transfer. These connectors keep the fibers aligned to avoid signal loss. Parts like ferrules and sleeves help them stay accurate during use.
There are many kinds of connectors, such as SC, LC, ST, and MTP. Over 100 types exist, split into single-mode and multi-mode groups. They are important in areas like telecom, data centers, and factories.
Why Are Fiber Optic Connectors Important?
Fiber optic connectors keep fiber systems working well and reliably. Bad connectors can cause signal loss and system problems. Good ones ensure smooth and steady communication.
The shape of a connector affects how well it works. A Corning Cable Systems report shows better shapes reduce signal loss. Polishing, as explained in "Polishing of Fiber Optic Connectors," makes surfaces smooth for better light flow.
Rules like Telcordia's GR-1081 guide how connectors are made and used. Picking the right connector improves cable performance and avoids costly fixes.
Common Applications of Fiber Optic Connectors
Fiber optic connectors are used in many fields. In telecom, they support fast internet and phone services. In 2022, telecom made up 42.5% of the market, growing in places like China and India.
In healthcare, they help with telemedicine and clear imaging systems. This area is growing by 7.4% each year. Railways use them for lighting, inspections, and medical needs.
Data centers rely on these connectors to handle lots of data. They are strong and work well, even in tough conditions, making them great for factories too.
Fiber Optic Connector Types
SC Connectors
SC connectors are very common and widely used. They work with both single-mode and multi-mode fibers, making them flexible. These connectors have a push-pull lock, which makes them easy to install and keeps them secure. SC connectors are great for quick setups in telecom and data centers.
They perform well and are dependable. SC connectors usually have low signal loss, under 0.5 dB, which keeps signals strong. They also support fast data transfer, making them good for long-distance use. Their tough design helps them work well even in harsh conditions.
Tip: For long-distance telecom systems, SC connectors are a solid option.
LC Connectors
LC connectors are small and fit in tight spaces. Their compact size makes them simple to use where space is limited. These connectors are popular in modern data centers and telecom systems because they work well with advanced tools.
LC connectors are reliable and perform better. They handle faster data speeds, making them ready for future tech. While they cost more upfront, they save money over time with lower running costs. The table below compares LC and SC connectors:
Aspect | LC Connectors | SC Connectors |
|---|---|---|
Compatibility Counts | Works well with modern devices | Fits more setups but needs more space |
Ease of Installation | Easy to use due to small size | Needs more room but is sturdy |
Future Proofing | Handles faster data speeds | Works well for many uses |
Cost Considerations | Higher initial cost, saves later | N/A |
Environmental Demands | Built to last | N/A |
Vendor Support | Trusted brands offer quality | N/A |
ST Connectors
ST connectors were once popular but are now less used. They have a bayonet-style lock that fits securely but isn’t as strong as newer designs.
ST connectors are less dependable than SC and LC connectors. They can lose signals if moved, causing problems with data flow. Many industries now prefer stronger and better options.
Note: If you need strong and reliable connectors, choose SC or LC instead of ST.
MPO/MTP Connectors
MPO and MTP connectors are useful in crowded places like data centers. They combine many fiber strands into one connector to make things simpler. These connectors help reduce cable mess in tight spaces, like server racks.
They work well for fast networks, such as 40G and 100G Ethernet. They support both single-mode and multi-mode fibers. For example:
40GBASE-SR4 and 100GBASE-SR4 use MPO connectors for quick data transfer.
MPO connectors with more fibers, like MPO-16 or MPO-24, work with advanced tools like 100GBASE-SR10 and 400GBASE-SR16.
These connectors save time in systems with many channels. Their easy-to-use design makes setup faster. Their small size also saves space in network setups.
Tip: MPO/MTP connectors are great for crowded and fast systems.
Other Fiber Optic Connector Types (e.g., FC, E2000)
Some connectors, like FC and E2000, are made for special uses.
FC Connectors
FC connectors are strong and send data quickly. They are common in data centers and SANs. These connectors are dependable and work well in tough places.
E2000 Connectors
E2000 connectors are easy to install because of their push-pull design. They are secure and simple to use, even if their speed details are not always clear.
Here’s a table comparing FC and E2000 connectors:
Connector Type | Data Speed | Cost | Where Used |
|---|---|---|---|
FC | Up to 64 Gbps | Affordable | Data centers, SANs |
E2000 | Not listed | Not listed | Not listed |
Choose the right connector based on your needs. FC connectors are good for fast data systems. E2000 connectors are better for easy handling and secure setups.
Note: Pick connectors that match your system for best results.
Key Factors in Choosing Fiber Optic Cables and Connectors
Compatibility
Matching the Connector to the Fiber Type
Picking the right connector is very important. It helps keep the signal strong. Different fibers, like single-mode or multi-mode, need specific connectors. Single-mode fibers work best with connectors for long distances and low signal loss. Multi-mode fibers need connectors for short distances and lower costs.
The cable type also matters for compatibility. Simplex cables have one optical strand and are good for direct connections. Multichannel cables have many strands and are better for places like data centers.
Ensuring Compatibility with Equipment
Connectors must match the devices in your network. Things like transmission mode, termination type, and polishing style affect compatibility. Experts suggest using connectors that fit both the cables and devices. This helps signals move smoothly and avoids problems.
Tip: Check that your connectors match your equipment to avoid mistakes.
Performance
Insertion Loss and Return Loss
Insertion loss and return loss show how well a connection works. Insertion loss measures signal loss when light passes through a connector. Return loss shows how much light bounces back. Lower numbers for both mean better performance.
Factory tests check connector quality using advanced methods. Field tests are simpler and check for dirt or damage. Single-mode fibers often have higher insertion loss because they go farther. Multi-mode fibers lose more signal over short distances.
Data Transmission Efficiency
Good connectors help data move smoothly. They reduce signal loss and keep the network working well. For fast systems like 40G or 100G Ethernet, MPO/MTP connectors are great. They handle high speeds and keep signals strong.
Note: Test and clean your connectors often to improve performance.
Cost
Balancing Budget and Quality
It’s important to balance cost and quality when choosing connectors. Cheap ones may not last or work well. Spending more on good connectors means fewer replacements and better performance.
Long-Term Cost Considerations
Think about long-term costs when picking cables and connectors. Strong connectors cost more at first but save money later. For example, outdoor cables with tough connectors last longer in bad weather.
Tip: Choose connectors that meet your needs and give good value.
Durability
Resistance to Environmental Conditions
When picking fiber optic connectors, think about the environment. Outdoor connectors face tough conditions like heat, cold, and moisture. They often have special coatings to handle these challenges. Some include water-blocking gels for underground use. These features help them work well in harsh weather.
Indoor connectors are different. They focus on being flexible and safe from fire. They don’t need UV or water protection. Instead, they meet fire safety rules for indoor spaces. Knowing these differences helps you choose the right connector for your needs.
Longevity in High-Use Applications
For heavy use, strong connectors are very important. They need to last long and work well. Frequent use can wear them out, causing problems. Choosing strong materials and designs helps them last longer. For example, connectors with sturdy locks stay reliable even with repeated use.
Taking care of connectors also makes them last longer. Clean and check them often to avoid damage. This keeps them working well and reduces replacements. Durable connectors save money and ensure steady performance over time.
Environmental Factors
Indoor vs. Outdoor Use
Choosing the right cables depends on where you’ll use them. Outdoor cables handle heat, cold, and sunlight. They have UV-resistant covers and water-blocking features. These make them great for tough conditions.
Indoor cables are made for flexibility and fire safety. They don’t need to handle bad weather but must meet fire safety rules. Using the wrong type can cause problems. Here’s a quick comparison:
Feature | Outdoor Cables | Indoor Cables |
|---|---|---|
Temperature Variance Tolerance | Made for extreme temperatures with special coatings. | Not designed for big temperature changes. |
UV Resistance | UV-resistant covers protect in sunlight. | Not UV-resistant; best for indoor use. |
Moisture Protection | Water-blocking gels help in wet areas. | Not for wet places; focus on fire safety. |
Fire Safety Standards | Not needed; outdoor cables skip fire safety ratings. | Must meet fire safety rules like plenum-rated. |
Design | Built for tough weather and outdoor use. | Compact and easy to install indoors. |
Temperature and Humidity Considerations
Temperature and humidity affect how fiber optics work. Outdoor connectors must handle big temperature changes and moisture. They use materials that resist these conditions to stay reliable. Indoor connectors don’t face these extremes. They focus on being flexible and meeting fire safety rules.
Think about the environment when choosing connectors. Pick ones that match the temperature and humidity of the area. This helps your network work better and last longer. By understanding these factors, you make smarter choices for your setup.
Single-Mode vs. Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Connectors
What Is Single-Mode Fiber?
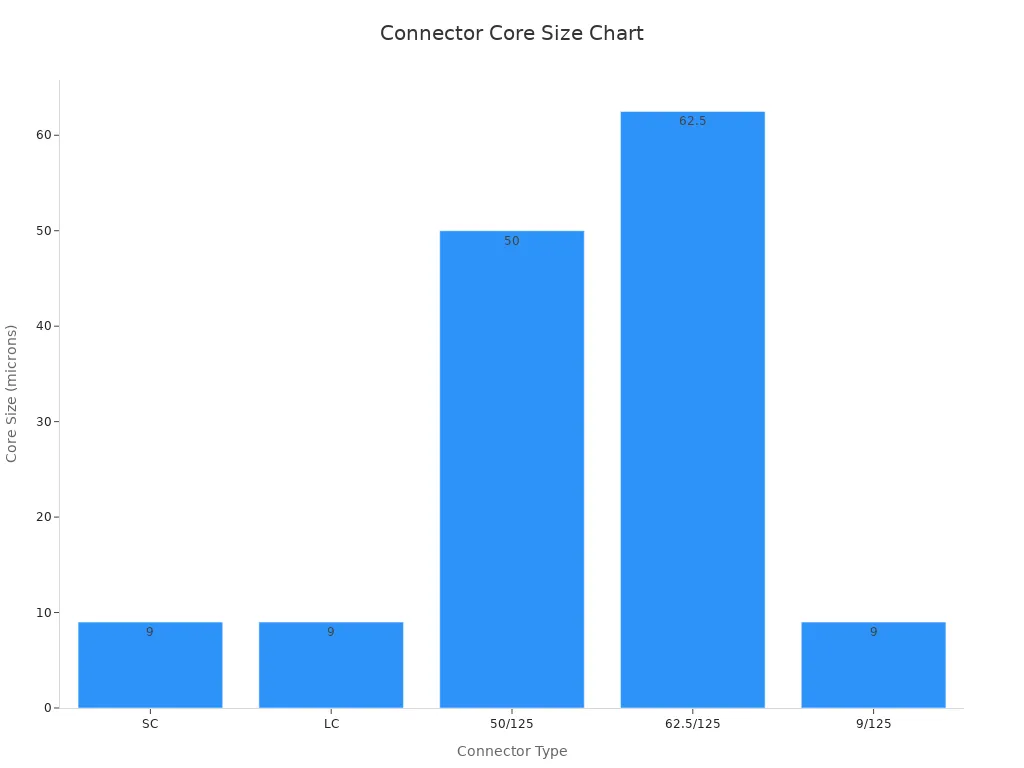
Single-mode fiber cables send data over long distances. They have a tiny core, about 9 microns wide. This lets light move straight, reducing signal loss. These fibers are great for far-away communication, like broadcasting. They can send data up to 30 kilometers and handle bandwidths of 100,000 GHz. Single-mode fibers cost more because they need lasers. However, their long-distance performance makes them worth it.
What Is Multi-Mode Fiber?
Multi-mode fiber cables are for short-distance data transfer. Their cores are bigger, around 50 or 62.5 microns. This allows multiple light paths, making them good for local networks and data centers. Multi-mode fibers are cheaper since they use LEDs. They work up to 2 kilometers and support bandwidths of 1 GHz. Their lower price and easy setup make them ideal for short-range use.
Key Differences Between Single-Mode and Multi-Mode Connectors
Knowing the differences helps you pick the right connector. Here’s a simple comparison:
Feature | Single-Mode | Multi-Mode |
|---|---|---|
Bandwidth | Up to 100,000 GHz | Up to 1 GHz |
Maximum Distance | Up to 30 kilometers | Up to 2 kilometers |
Connection Loss | Lower due to smaller core size | Higher due to larger core size |
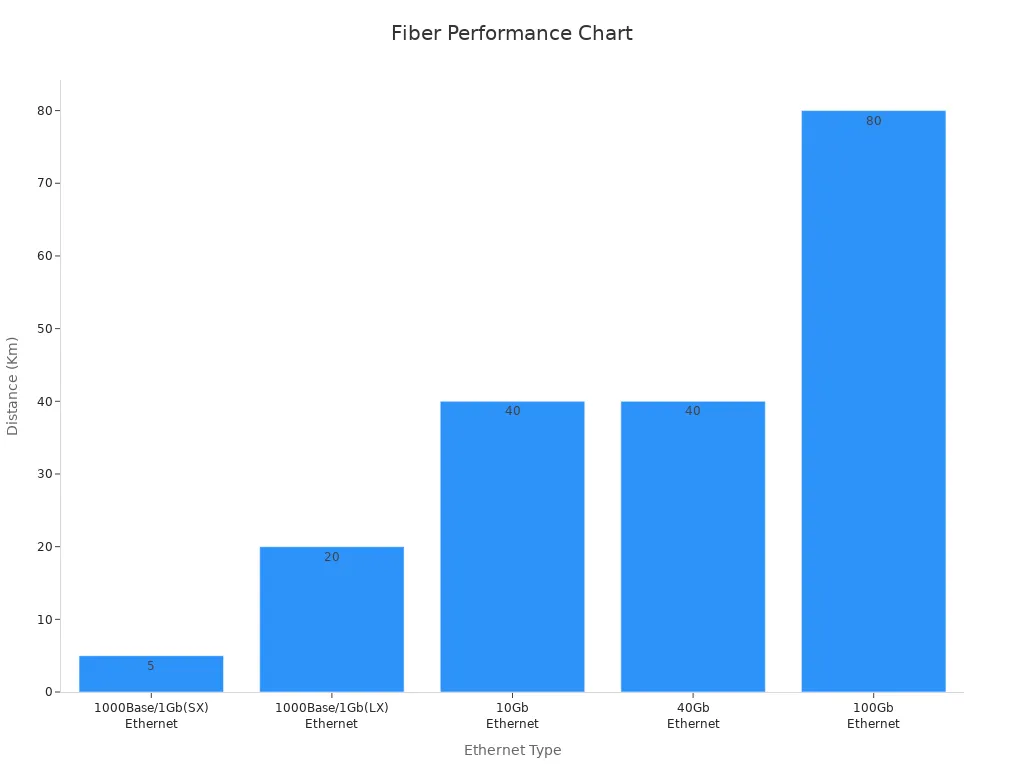
Single-mode fibers are best for long distances, like 40Gb or 100Gb Ethernet. They can reach up to 80 kilometers. Multi-mode fibers are better for short distances, like 10Gb Ethernet, with a limit of 550 meters. The table below shows how they perform:
Fiber Type | 1000Base/1Gb(SX) | 1000Base/1Gb(LX) | 10Gb Ethernet | 40Gb Ethernet | 100Gb Ethernet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Single-Mode | 20 km | 40 km | 40 km | 80 km | |
Multi-Mode (OM1) | 275 m | 550 m | 33 m | N/A | N/A |
Think about your network's distance and speed needs. Single-mode fibers are better for long distances. Multi-mode fibers are cheaper and work well for short connections.
When to Use Single-Mode vs. Multi-Mode Connectors
Choosing between single-mode and multi-mode connectors depends on your network's needs. Each type has specific uses, so knowing their benefits helps you decide.
Single-mode connectors are best for long distances. They work well for broadcasting, telecom, and big data transfers. These connectors pair with single-mode fibers, which send data up to 30 kilometers. Their small core reduces signal loss, making them great for high-bandwidth tasks. However, they cost more because of the advanced technology needed.
Multi-mode connectors are better for short distances. They are common in offices, data centers, and local networks. Multi-mode fibers have larger cores, allowing multiple light paths. This makes them cheaper and easier to set up. They work well up to 2 kilometers, making them a budget-friendly choice for short connections.
Tip: Choose single-mode connectors for long distances and high bandwidth. Use multi-mode connectors for short, cost-effective setups.
Here’s a simple comparison:
Feature | Single-Mode Connectors | Multi-Mode Connectors |
|---|---|---|
Best Use Case | Long-distance communication | Short-range connectivity |
Maximum Distance | Up to 30 kilometers | Up to 2 kilometers |
Bandwidth | Up to 100,000 GHz | Up to 1 GHz |
Cost | Higher due to advanced optics | Lower, more economical |
Studies show single-mode fibers are best for long-distance tasks. They are key in telecom where reliability over long ranges is vital. Multi-mode fibers are ideal for short-range setups like data centers, where cost and simplicity matter.
Think about your network's distance and speed needs. Single-mode connectors are great for long-distance performance. Multi-mode connectors are better for short, affordable connections. Matching your choice to your network ensures good performance and value.
Best Practices for Installation and Maintenance of Fiber Optic Connectors
Proper Installation Techniques
Cleaning and Preparing the Fiber
Before installing fiber optic connectors, clean the cables carefully. Dirt, oil, or fingerprints can weaken signals and hurt performance. Use special tools like lint-free wipes and alcohol to clean them. Always check the fiber ends with a microscope to ensure they are spotless.
To avoid damaging cables, roll them off the spool gently. Don’t pull them directly. For long cables, use a figure 8 pattern to prevent twists. This keeps the cables stress-free and ready to work well.
Ensuring Proper Alignment
Aligning connectors correctly is very important for good signals. Misaligned connectors can cause signal loss and poor data flow. Use alignment tools and follow the maker’s instructions for a secure fit.
Make sure all parts are ready before starting. Hiring trained installers, like FOA-certified ones, ensures proper work. Following rules like NECA/FOA 301 helps make the installation reliable and efficient.
Maintenance Tips
Regular Cleaning and Inspection
Clean and check fiber optic connectors often to keep them working well. Look for dirt, dust, or fingerprints on the connectors. Use tools like inspection scopes to check the ends. Clean them with special kits to keep signals clear and strong.
Label each cable during installation to make future checks easier. Advanced systems with scanning tools can also help track and maintain cables better.
Replacing Damaged Connectors
Broken connectors can harm your network. Replace any with scratches or cracks. Ignoring damaged connectors can cause signal problems. Test and check cables regularly to find and fix issues quickly.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding mistakes during installation and maintenance saves time and effort. One common mistake is not checking connector ends for dirt. Dirty connectors can cause bad performance. Always clean and inspect them before and after use.
Another mistake is bending cables too much. This can weaken signals. Pull cables gently to keep the right bend shape. Also, follow safety rules, like wearing protective gear, to avoid risks during tasks like splicing.
Note: Careful steps during installation and maintenance keep connectors working well. Following safety rules and standards reduces risks and improves performance.
Picking the right fiber optic connector helps your network work well. Things like compatibility, performance, and strength are important to choose wisely. For instance, LC connectors are great for fast and growing networks. SC connectors are strong and work with many systems. Think about the environment, like heat and moisture, when deciding.
Here’s a simple guide for common fiber optic connectors:
Type of Connector | How It Connects | Fiber Count | Polishing Style | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Ferrule Connector (FC) | Screw Lock | 1 | PC/UPC/APC | Local networks |
ST | Twist Lock | 1 | PC/UPC | Telecom systems |
Standard Connector (SC) | Push-Pull Lock | 1 | PC/UPC/APC | TV and security systems |
LC | Push-Pull Lock | 1 | PC/UPC/APC | Fast Ethernet connections |
MU | Push-Pull Latch | 1 | PC/UPC/APC | Military fiber networks |
MT-RJ | Twist Lock | 2 | N/A | Data transfer systems |
MT | Push-Pull Latch | 4 to 24 | N/A | Big networks and devices |
When choosing, keep these tips in mind:
Make sure it matches your network tools.
LC connectors are simple to set up and handle fast speeds.
SC connectors are tough and useful for many tasks.
Check the environment to pick durable options.
If you’re not sure what you need, ask an expert. The right connector will improve your fiber optic system and keep it running well for a long time.
FAQ
What does a fiber optic connector do?
It connects two fiber cables for smooth data transfer. It keeps the fibers lined up to reduce signal loss and ensure good performance.
How can you pick the right fiber optic connector?
Think about compatibility, cost, durability, and performance. Match it to your fiber type and devices. Check if it’s for indoor or outdoor use to make sure it works well.
Can fiber optic connectors be reused?
Yes, if they are not damaged. Clean and check them carefully before using again. Replace broken ones to avoid problems.
How often should fiber optic connectors be cleaned?
Clean them often, especially if used a lot. Dirt can hurt performance. Use special cleaning tools and check them after cleaning to keep them working well.
What’s the difference between single-mode and multi-mode connectors?
Single-mode connectors are for long distances with less signal loss. Multi-mode connectors are cheaper and better for short distances. Choose based on how far and fast your network needs to go.
Are fiber optic connectors made for tough weather?
Some are built for outdoor use and can handle heat, cold, and moisture. Indoor ones don’t have these features but meet fire safety rules. Pick based on where you’ll use them.
Can bad installation harm fiber optic connectors?
Yes, it can cause misalignment, damage, or signal loss. Follow the maker’s instructions and use the right tools for a proper fit.
Do fiber optic connectors affect how fast data moves?
Yes, good connectors help keep data moving fast. They lower signal loss and work well in high-speed networks like 40G or 100G Ethernet.
